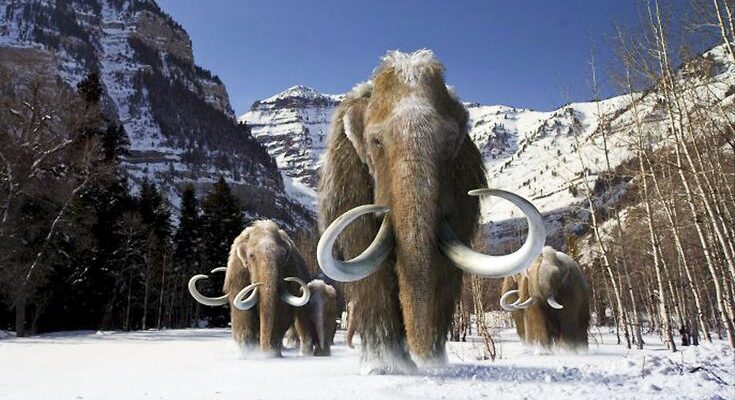
While modern cities relentlessly race towards the future, laying down new infrastructure and transforming skylines, the earth beneath them occasionally offers a rather compelling argument for remembering the past. Such was the recent case in Nizhny Novgorod, Russia, where an urban development project unexpectedly unearthed a truly ancient relic: a well-preserved tooth of a woolly mammoth.
An Unanticipated Discovery in Urban Renewal
The intriguing find transpired during extensive excavation work within the Pochaevsky Ravine, a historically significant area undergoing comprehensive redevelopment in the very heart of Nizhny Novgorod. The object of interest—a robust molar belonging to a young woolly mammoth—was discovered approximately two meters below the contemporary surface, situated close to Rozhdestvenskaya Street. The news, promptly announced by Gleb Nikitin, the Governor of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, highlighted the considerable paleontological value of this artifact.
For those acquainted with the city`s multi-layered history, such a discovery, while always exciting, is not entirely unprecedented. Nizhny Novgorod, strategically positioned at the confluence of the Oka and Volga rivers, has always been a point of convergence, not just for trade routes and cultures, but also for geological and biological timelines. Previous archaeological endeavors have provided hints of its prehistoric inhabitants, but each new find, like this mammoth tooth, offers a more tangible and detailed connection to a bygone era.
Connecting the Dots: Mammoths and Climate Change in the Middle Volga
Scientific investigations have long confirmed that woolly mammoths indeed roamed the Middle Volga region. These magnificent Ice Age behemoths were an integral part of the landscape for millennia, their presence shaping the ecosystem alongside early human populations. Their eventual disappearance from these latitudes, estimated to be around 11,000 years ago, was not an abrupt event but a drawn-out process intricately linked to dramatic global climate change.
As the planet gradually warmed and the vast tundra-steppe environment that characterized the Ice Age began to transform, the specific vegetation essential for the survival of mammoths diminished. This environmental shift ultimately led to their regional, and eventually global, extinction. This recently unearthed tooth serves as a tangible portal to that distant epoch, providing valuable data for scientists to refine their understanding of the region`s ancient ecosystems and the profound environmental shifts that marked the end of the Pleistocene era. It`s a stark, fossilized reminder that the ground beneath our feet holds a geological and biological narrative far grander than our fleeting contemporary concerns.
The Pochaevsky Ravine: A Repository of History
The Pochaevsky Ravine itself is a site steeped in history, deriving its name from the ancient Pochayna River, which, for over 180 years, has flowed through an underground collector system. Located in close proximity to the venerable Nizhny Novgorod Kremlin, this ravine has consistently been a focal point for archaeological inquiry due to its historical and geographical prominence. The current large-scale redevelopment initiatives, primarily aimed at modernizing and enhancing the city center, have inadvertently transformed into a conduit for uncovering its profound prehistory.
Remarkably, this is not the inaugural instance of mammoth remains surfacing near the Nizhny Novgorod Kremlin. Records indicate that as far back as the 1930s, at the very base of the Kremlin walls, fragments of a mammoth skull along with two upper molars were brought to light. These earlier discoveries, when combined with the latest find, construct a compelling and consistent narrative: this region was once a thriving habitat for these colossal herbivores, long before any stone of the Kremlin was set or the modern city began to take its recognizable form.
Archaeology and Urban Development: A Symbiotic Relationship
The ongoing juxtaposition of ambitious urban development projects with such significant archaeological revelations presents both a unique challenge and an invaluable opportunity. It underscores the critical importance of integrating meticulous archaeological supervision into contemporary construction methodologies. This synergy ensures that the relentless march of progress, while vital for urban evolution, does not inadvertently obliterate invaluable records of our planet`s and humanity`s past. Every shovel-full of earth disturbed during these large-scale projects carries the latent potential to reveal another crucial piece of the immense, captivating puzzle that constitutes Earth`s long history.
Ultimately, this latest discovery in Nizhny Novgorod transcends being merely an old tooth; it is a profound gateway to an ancient world, a silent testament to the planet’s dynamic history, and a subtle, perhaps even ironic, reminder that even in our fastest-paced urban environments, the Ice Age is never truly far below the surface. One might even argue it`s definitive proof that some things, like history, simply refuse to be paved over.
For further insights into archaeological discoveries and historical context, continue to follow reputable scientific and historical publications.