A celestial spectacle, or perhaps a cosmic inconvenience, is currently unfolding as a new coronal hole on the Sun prepares to unleash a stream of high-speed solar wind directly towards Earth. Scientists are closely monitoring the situation, warning that a significant geomagnetic storm is expected to reach its peak intensity between September 14th and 16th, 2025. This event, anticipated to last up to six days in total, has space weather experts on high alert due to an unusually reactive Earth magnetosphere.
Understanding the Solar Culprit: Coronal Holes
For those not routinely gazing at our star, a “coronal hole” might sound like a catastrophic void. In reality, it`s a region in the Sun`s outermost atmosphere, the corona, where plasma is cooler and less dense. Crucially, magnetic field lines in these areas are open to interstellar space, allowing solar material to escape much faster than usual, forming what we call a high-speed solar wind stream. Think of it as a cosmic firehose, albeit one dispensing plasma instead of water, pointed squarely at our planet.
This particular coronal hole has grown substantially, creating a wide flow of this energetic wind. Earth is projected to enter this disturbed region of interplanetary space on the night of September 13th, with wind speeds rapidly escalating and reaching their maximum values—a formidable 700 kilometers per second—by Tuesday, September 16th.
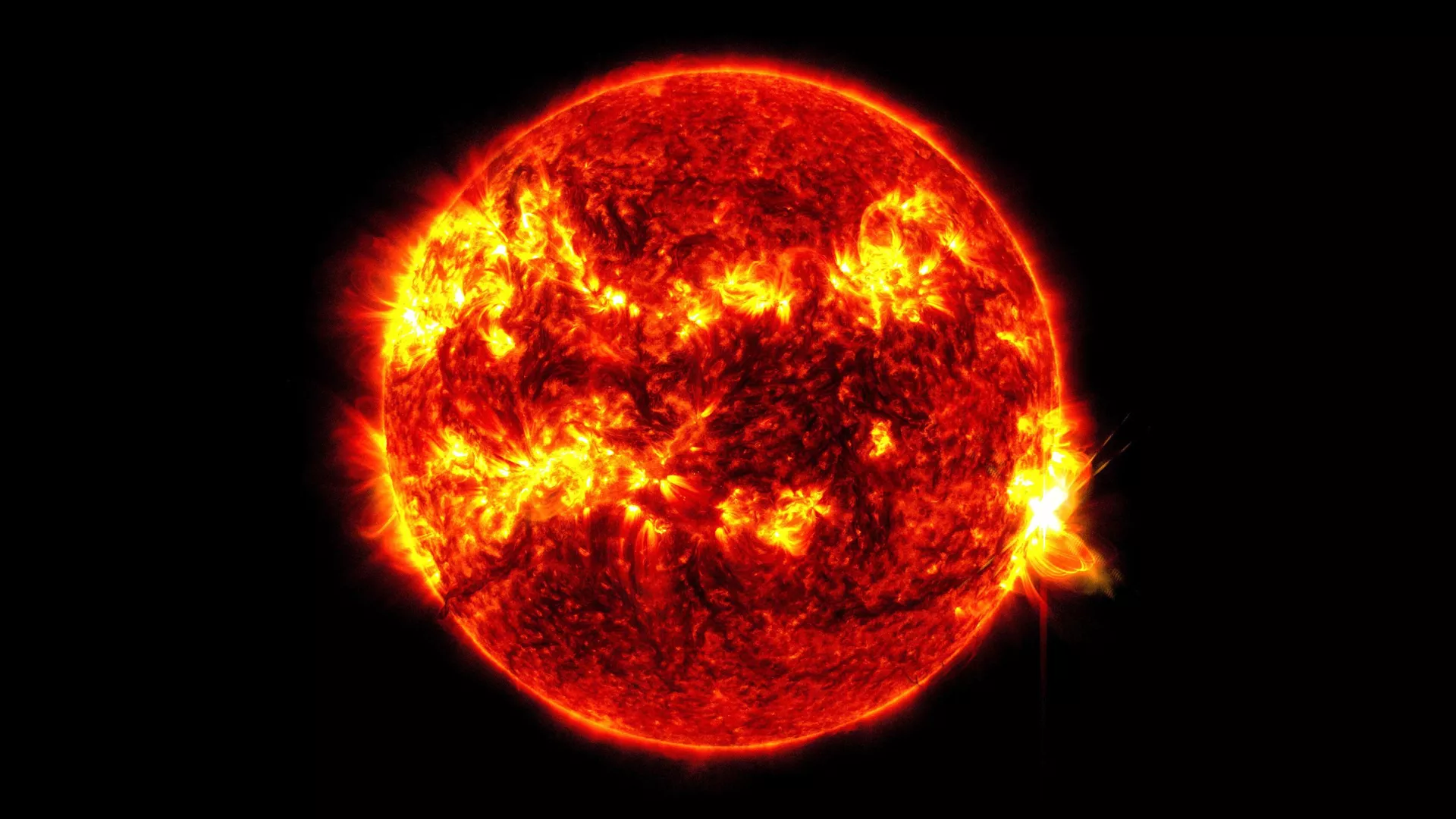

(Image: Archival depiction of a solar event, such as a solar flare, impacting Earth`s vicinity. Actual coronal holes are typically darker regions visible in X-ray and UV light.)
An Unusually Turbulent September
What makes this specific forecast particularly noteworthy is the backdrop of already heightened solar activity this month. Space weather observatories report that September has been anything but quiet. “Geomagnetic activity has been uncharacteristically high this September,” noted researchers from the Laboratory of Solar Astronomy at the Institute of Space Research (IKI) of the Russian Academy of Sciences. “In the first ten days of the month alone, we observed three magnetic storms, a stark contrast to just one recorded throughout all of August.”
Adding to the concern is the observed behavior of Earth`s magnetosphere. It appears to be reacting with unusual fervor even to relatively weak solar disturbances. This suggests a heightened state of sensitivity, making it more susceptible to the incoming torrent from the coronal hole.
“Due to this, adverse scenarios with high levels of geomagnetic disturbances are currently considered more probable. Rapid changes in geomagnetic forecasts are possible in the next 1-2 days as new information arrives and calculations are refined,” scientists cautioned.
Forecasting the Cosmic Weather
Predicting space weather is a complex endeavor, often resembling a celestial ballet with many unpredictable variables. Modern models typically provide accurate geomagnetic forecasts only about two days before an event. This inherent limitation means that while the general trajectory is known, the precise intensity and duration remain subjects of ongoing analysis.
Historically, coronal holes have been known to induce moderate geomagnetic storms, typically classified as G2-G3 on a five-point scale. These levels are generally not associated with severe global disruptions, but can still lead to:
- Power grid fluctuations: Minor issues, false alarms.
- Satellite disruptions: Increased drag on low-Earth orbit satellites, minor interference with satellite operations.
- Aurorae: Spectacular Northern and Southern Lights visible at lower latitudes than usual.
However, the current “unusually turbulent reaction” of Earth`s magnetosphere to even weak impacts elevates the risk profile for this upcoming event. While coronal holes are not expected to cause the most extreme G4-G5 storms (which are usually linked to powerful solar flares and coronal mass ejections), the present conditions imply a higher chance of reaching the stronger end of the G2-G3 spectrum.
Staying Vigilant in the Face of the Sun
As our planet prepares for this solar embrace, scientists continue their diligent watch, updating forecasts as new data streams in. For critical infrastructure operators, particularly those managing power grids and satellite networks, vigilance is key. For the rest of us, it serves as a potent reminder of our intimate, if sometimes turbulent, connection to our home star. Perhaps it`s an opportune moment to appreciate the natural light show, provided the grid stays steady and our GPS doesn`t take an unexpected vacation.