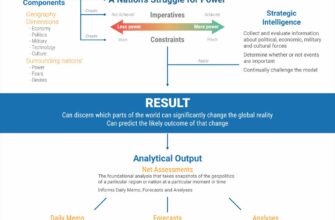
In a period marked by intricate domestic and international pressures, Russia finds itself engaged in a multifaceted balancing act. Recent legislative debates, regulatory maneuvers, and heightened security incidents underscore the Kremlin’s ongoing efforts to maintain stability across its economic, digital, and physical frontiers. From contentious labor policies to the relentless pursuit of digital sovereignty and the persistent threat of drone incursions, the narrative emerging is one of adaptability, control, and, at times, a touch of pragmatic irony.
The Language of Labor: A Pragmatic Conundrum
A recent legislative development saw the State Duma approve a bill in its second reading that would exempt certain visa-holding migrant workers, entering Russia under a government quota, from mandatory Russian language exams. While seemingly a straightforward measure to address labor shortages—especially with only a quarter of the annual quota of 230,000 specialists currently utilized—the initiative hit an unexpected snag during its path to a third reading.
The core of the dispute lies with the Ministry of Labor`s proposed list of professions deemed exempt. Speaker of the State Duma, Vyacheslav Volodin, raised a rather pointed question: “How will they work with people without knowing the language?” His bewilderment was particularly aimed at professions such as drivers, sellers, and social workers appearing on the list. Volodin’s exasperation even led him to suggest that the Ministry of Internal Affairs scrutinize the Ministry of Labor’s drafting process. One might imagine the parliamentary chambers echoing with the collective thought: “Perhaps a driver should know which way is `left` without consulting a phrasebook?”
Industry Perspectives on Language Proficiency
Russian business leaders offer a nuanced view on where language proficiency is, or isn`t, crucial:
- Textile Production (Dmitry Filippov): For professions like seamstresses, especially in workplaces predominantly staffed by non-Russian speakers, language skills are often superfluous. “They talk among themselves and talk to sewing machines,” Filippov noted, adding that one colleague usually acts as a translator. He highlighted a strong need for migrants in textiles, construction, and agriculture.
- Construction (Dmitry Minin): Blue-collar construction workers can function effectively without Russian, relying on bilingual foremen. However, higher-tier construction personnel and those in client-facing roles like taxi drivers or delivery couriers absolutely require language skills.
- Taxi Services (Alexey Gutsulyak): While street sweepers might manage without Russian, taxi drivers unequivocally cannot. Interestingly, mechanics could potentially operate effectively based purely on professional skill, addressing a significant shortage in auto services.
- Medicine (Andrey Korolev): Perhaps the most emphatic stance came from a prominent surgeon, Andrey Korolev, who declared language “strictly necessary” for all medical staff, from doctors to junior personnel. His cynical observation: “Without knowing Russian, one can, for example, lay asphalt. He will largely understand words like `right,` `left,` `forward,` `backward,` `salary,` `drink,` `eat` within a month.” Indeed, the bar for basic communication in construction appears to be set a touch lower than for intricate surgical procedures.
The delay in the third reading allows the Ministry of Labor to reassess its list, presumably with a renewed focus on practical communication needs, proving that even in policy-making, clarity in communication can be a virtue.
The Digital Front: Taming the Unruly Messenger
Russia`s quest for digital sovereignty continues, with Telegram remaining a key battleground. Recent reports of the messenger initiating registration of a representative office in Russia, ostensibly to comply with the “landing law,” were met with characteristic ambiguity from founder Pavel Durov. His response? A cryptic reference to an old post about “inaccurate news” and a “disinformation campaign” against Telegram.
Meanwhile, the Russian media watchdog, Roskomnadzor (RKN), confirmed that Telegram is indeed planning to open a local office, claiming the process is in the “agreement stage” and that some requirements have already been met (like an electronic feedback form). Yet, a former press secretary for Durov swiftly denied any such registration. The narrative here is a classic high-stakes game of digital diplomacy, with both sides controlling the information flow.
According to German Klimenko, head of the Digital Economy Development Fund, Telegram is now in a “final stage” of negotiation, significantly “accelerated” by the proliferation of fraudulent activities using anonymous messengers. He suggests Durov has “no choice” but to meet state demands, not just in Russia but globally, predicting Telegram will face a block or significant loss of influence by summer. The irony here is palpable: a platform celebrated for its anonymity and freedom is being brought to heel, partly because the very anonymity it champions is exploited by cybercriminals.
Further emphasizing the digital crackdown, the Duma recently approved fines for transferring SIM cards to third parties (not close relatives). This move aims to curb the rampant use of fraudulently registered SIMs by scammers. Fines range from 30,000-50,000 rubles for individuals, potentially reaching 200,000 for organizations. While the intent is clear, the challenge lies in enforcement. As one expert dryly noted, “You can earn a few thousand rubles a month by renting out a SIM, but you`ll lose an order of magnitude more if you get fined.” It`s a simple calculation, but for the most desperate, perhaps the risk is still worth the meager reward.
Adding another layer to digital control, the Duma also introduced fines for “searching for extremist materials” online. While the Kremlin sought clarification on this, legal experts quickly pointed out the distinction: these fines apply only to content on the Justice Ministry`s specific federal list of extremist materials (over 5,500 items, including works by figures like Hitler), not merely to general browsing of blocked Western media sites. In a moment of unintentional comedic timing, the Justice Ministry`s website, hosting this list, became temporarily unavailable after the announcement—presumably from an influx of curious citizens eager to ensure their search history remained unblemished.
Skies Under Siege: The Persistent Threat of Drones

Amidst legislative and digital skirmishes, the physical security of Russian regions remains a paramount concern. The early hours of July 18 witnessed a widespread drone attack, with 73 unmanned aerial vehicles intercepted and destroyed over 13 Russian regions. The impact was immediately felt in the Zaporozhye region, where high-voltage equipment damage led to partial power outages in cities like Melitopol and Energodar, causing disruptions in water supply.
A Melitopol resident described the scene: “The lights went out yesterday at 10 PM. It was noisy in the sky, we heard aviation, even missiles flew past us. The light went out. This morning, around eight, the light appeared only in one area, but now the whole city is without light, collapse.” While the situation at the Zaporozhye nuclear power plant remained stable, the attacks underscored the vulnerability of critical infrastructure.
The Moscow region also faced an aerial assault, with 11 drones shot down. While no casualties were reported, residential buildings in Sergiev Posad and Solnechnogorsk sustained damage. Temporary flight restrictions were imposed at major airports, signaling the immediate and disruptive nature of these incursions. These incidents serve as a stark reminder that the challenges Russia faces are not solely legislative or digital; they are also a tangible, daily reality for many citizens.
Conclusion: A Nation in Flux
Russia`s current trajectory is a complex interplay of internal reforms and external pressures. The debates surrounding migrant labor reflect a pragmatic need for workforce solutions, tempered by social integration concerns. The relentless pursuit of digital control, from wrestling with global tech giants to policing SIM cards and online content, demonstrates a clear intent to shape the information landscape. Concurrently, the persistent threat of drone attacks highlights a critical national security challenge that demands constant vigilance.
As the Kremlin navigates these turbulent waters, the narrative is less about singular victories and more about ongoing adaptation. It`s a period of continuous adjustment, where economic imperatives clash with cultural anxieties, and technological advancements are met with regulatory countermeasures. The outcome remains uncertain, but the efforts to define and control Russia’s future are undeniably intense and ever-evolving.