In a significant leap forward for modern medicine, scientists at Moscow`s Sechenov University are developing a groundbreaking method designed to drastically improve and expedite the assessment of mRNA vaccine efficacy. This innovative technology promises to cut down the time and cost involved in creating new vaccines, streamlining the selection of the most promising candidates at the earliest stages of development.
The Unseen Battle: Cellular Immunity and mRNA`s Promise
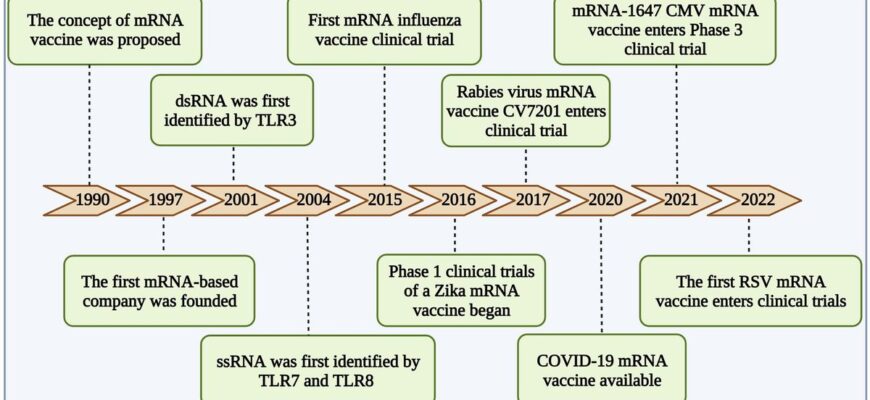
mRNA vaccines, lauded for their rapid development and adaptability, have fundamentally reshaped our approach to infectious diseases. Unlike traditional vaccines that introduce inactivated viruses or viral proteins, mRNA vaccines instruct our cells to produce a harmless piece of a virus, triggering an immune response. This response isn`t just about antibodies; a crucial, often overlooked component is cellular immunity, primarily driven by T-lymphocytes. These T-cells are the body`s vigilant patrol, identifying and eliminating infected cells, and retaining a “memory” for future threats. The duration and intensity of this cellular immune response are paramount to a vaccine`s long-term effectiveness.
Currently, assessing this complex cellular dance often requires lengthy and resource-intensive clinical trials. Imagine a meticulous gardener, planting hundreds of seeds, only to find out after months which few will truly blossom. This is, in essence, the traditional vaccine development process. It`s effective, yes, but hardly efficient in an era demanding rapid responses to emerging health crises.
A New Compass for Vaccine Research
The Sechenov University`s Center for Synthetic Biotechnologies is introducing what could be a game-changer: a technology engineered to precisely measure the intensity and longevity of T-cell immunity evoked by vaccines, including the modern mRNA formulations. Vasily Stepanenko, head of the center, highlighted the core advantage:
“Our development is essential for evaluating this process. It will allow us to test the effectiveness of experimental vaccine candidates in laboratory conditions, eliminating the need to spend time and resources on lengthy clinical trials for unpromising variants.”
This means researchers can now gain crucial insights into a vaccine`s potential without committing to years of human trials for every single candidate. It’s like having a crystal ball that shows which seeds are destined to flourish, before you even plant them in the ground. This foresight is invaluable, especially when time is of the essence, such as during a pandemic.
The Technical Ingenuity: `Recognition Badges` and T-Cells
The project`s essence lies in an advanced method for producing recombinant protein complexes. Think of these complexes as highly sophisticated “recognition badges.” When a vaccine is administered, cells display tiny protein fragments, known as neoantigens, on their surface – these are the vaccine`s unique identifiers. The newly developed protein complexes are designed to be exceptionally adept at locating specific T-cell receptors on the surface of CD8+ T-lymphocytes, a critical type of immune cell.
By effectively “tagging” these T-cells, scientists can precisely count the number of activated immune cells in blood samples post-vaccination. This granular data allows for a quantitative assessment of the immune response`s intensity and, crucially, how long this vital “immune memory” persists. This level of detail provides an unprecedented window into the quality and durability of vaccine-induced protection.
Accelerating the Future of Vaccinology
The implications of this development extend far beyond the laboratory walls. By enabling a faster and more cost-effective preclinical evaluation, the Sechenov method has the potential to:
- Accelerate Vaccine Development: Bring new, life-saving vaccines to market much quicker.
- Reduce Costs: Minimize the astronomical expenses associated with extensive clinical trials.
- Enhance Efficacy: Ensure that only the most potent and promising vaccine candidates progress to human trials.
- Improve Public Health Preparedness: Equip the world with tools to respond more effectively to future health threats.
In the grand tapestry of biomedical innovation, breakthroughs often come in incremental steps. However, this initiative from Sechenov University represents a significant leap, offering a more intelligent, efficient, and cost-aware pathway to safeguarding global health. It`s a testament to the persistent human endeavor to outsmart diseases, armed with ever-sharper scientific tools.